China COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker
(No longer being updated since December 28, 2022)
Our follow-up project – China’s Emerging Global Vaccine Footprint – looks at how China and other countries are supporting local vaccine manufacturing in the post-COVID era.
Since the outbreak of the pandemic, China has committed to making its COVID-19 vaccines a global public good. On multiple occasions, high-level Chinese officials have declared that China is fulfilling this pledge by exporting and donating its COVID-19 vaccines to as many countries that it can. This has generated a great deal of interest and discussion amongst experts from various fields. As an independent, mission-driven consultancy that tracks China’s impact on global health, Bridge Consulting aims to examine and offer a comprehensive picture of China’s vaccine outreach, hopefully enabling more informed discussions on this issue worldwide.
Read more about our methodology here.
1.853B (+0M) DOSES SOLD
328M (+0M) DOSES DONATED
1.653B (+0M) DOSES DELIVERED
Updated as of 13:00 pm (GMT+8), December 28, 2022.
This tracker is no longer being updated.
It includes all bilateral and multilateral sales, donations, and deliveries that have been officially reported through publicly accessible sources.
Contents
- 1 Total and Weekly Tracker Highlights
- 2 China’s Vaccines Around the World
- 3 Timeline of Vaccines Delivered by China
- 4 China’s Vaccines Across Regions
- 5 Top 10 Doses Delivered, Purchased, and Donated
- 6 China’s Multilateral Vaccine Contributions
- 7 COVAX Deliveries of Chinese Vaccines
- 8 China’s Vaccines by Manufacturers
- 9 Overseas Manufacturers of Chinese Vaccines
- 10 Notes
- 11 Methodology
Total and Weekly Tracker Highlights
-
- Africa Update: Total Sales – 126.4M (+0) | Total Pledged Donations – 152.8M (+0) | Total Deliveries – 153.2M (+0)
- Asia Pacific Update: Total Sales – 944.9M (+0) | Total Pledged Donations – 143M (+0) | Total Deliveries – 909.8M (+0)
- Europe Update: Total Sales – 123.5M (+0) | Total Pledged Donations – 5.6M (+0) | Total Deliveries – 59.5M (+0)
- Latin America Update*: Total Sales – 397.9M (+o) | Total Pledged Donations – 13.4M (+0) | Total Deliveries – 296.8M (o)
- COVAX Update*: Total Sales – 259.8M (+0) | Total Deliveries – 234.0M (+0)
*Weekly updates in brackets.
China’s Vaccines Around the World
This interactive map tracks the vaccine sales and donations that China and Chinese vaccine developers have made. It also tracks the number of delivered vaccines.
Timeline of Vaccines Delivered by China
Multiple global developments have impacted the amount of Chinese COVID-19 vaccine deliveries over time. The timeline illustrates the deliveries made to various countries since the beginning of the pandemic and below are some notable events since China started exporting COVID-19 vaccines in 2020.
Notable Events Impacting China’s Vaccine Delivery:
MoreChina’s Vaccines Across Regions
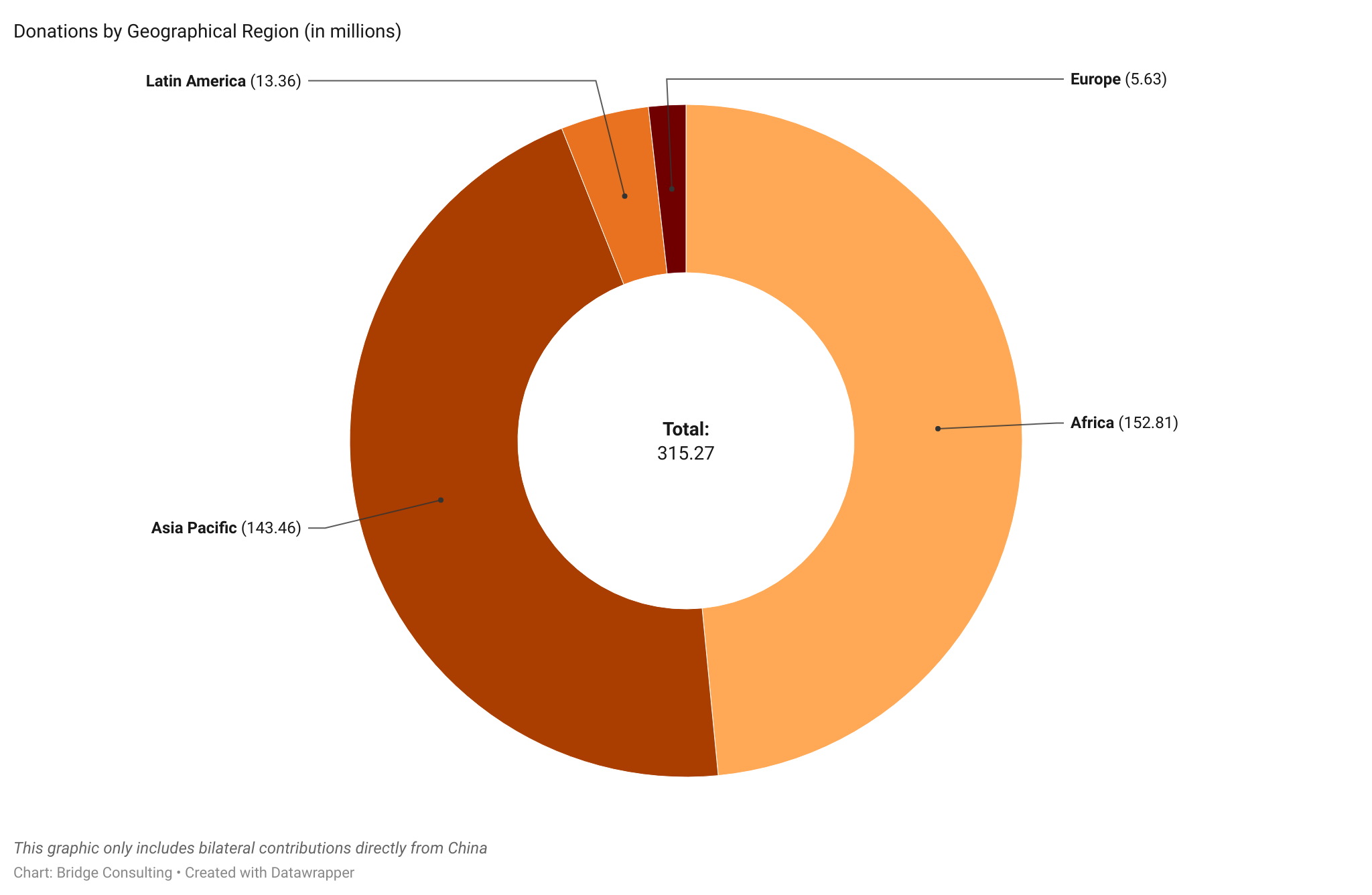
China has directly provided vaccines to four geographical regions – a total of 119 countries around the world. Out of these four regions, Asia Pacific has received the most significant number of Chinese vaccines, with 39 countries receiving vaccines from China. Latin America has received the second most considerable number of Chinese vaccines, though only 22 countries have received them. In contrast, while Africa has 48 countries receiving vaccines from China, the region has received few Chinese vaccines.
Take a look at our slideshow below to see deliveries, sales, and donations of Chinese vaccines by Geographical Region.
Please press the arrows below to alternate between graphs.
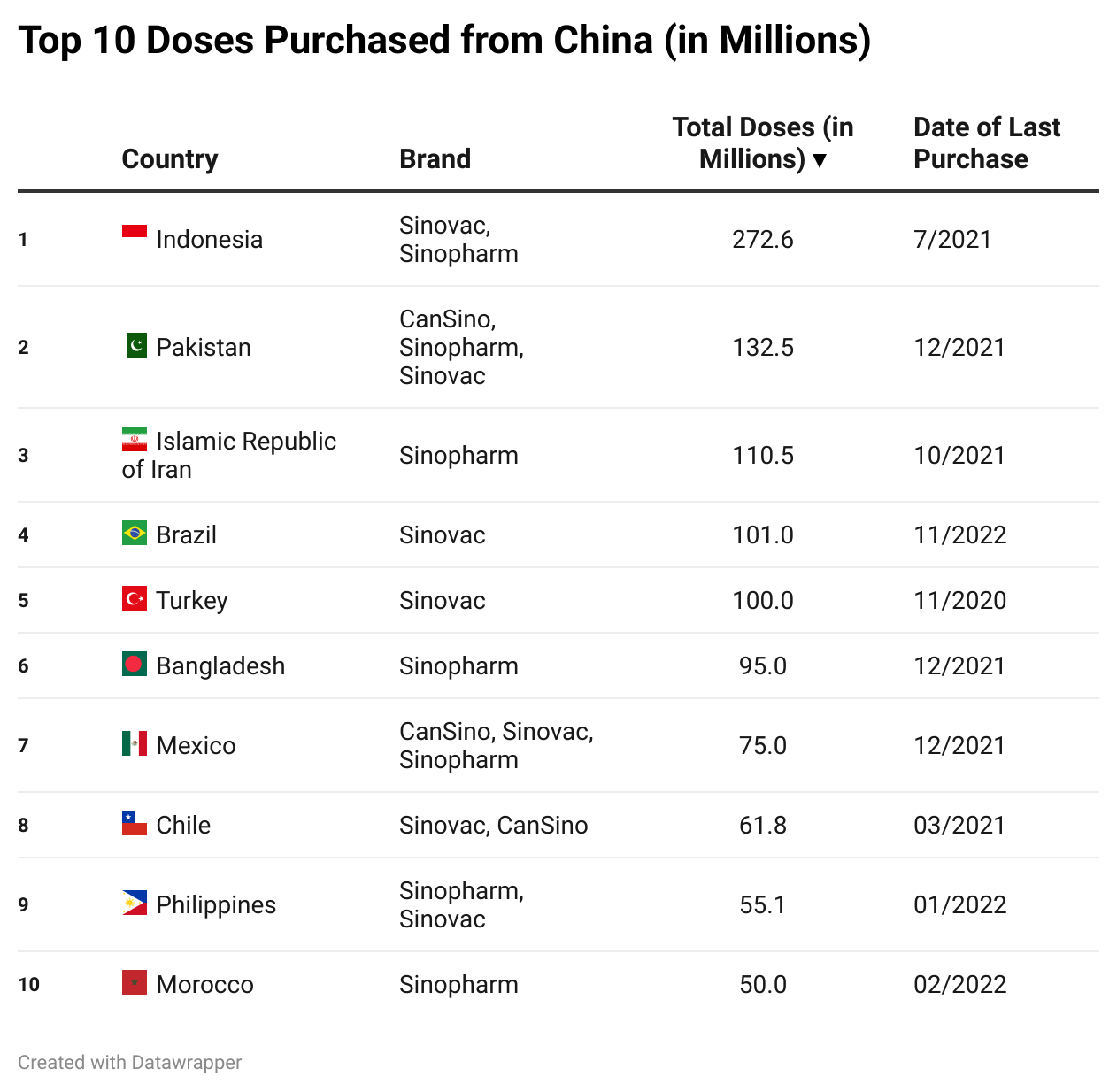
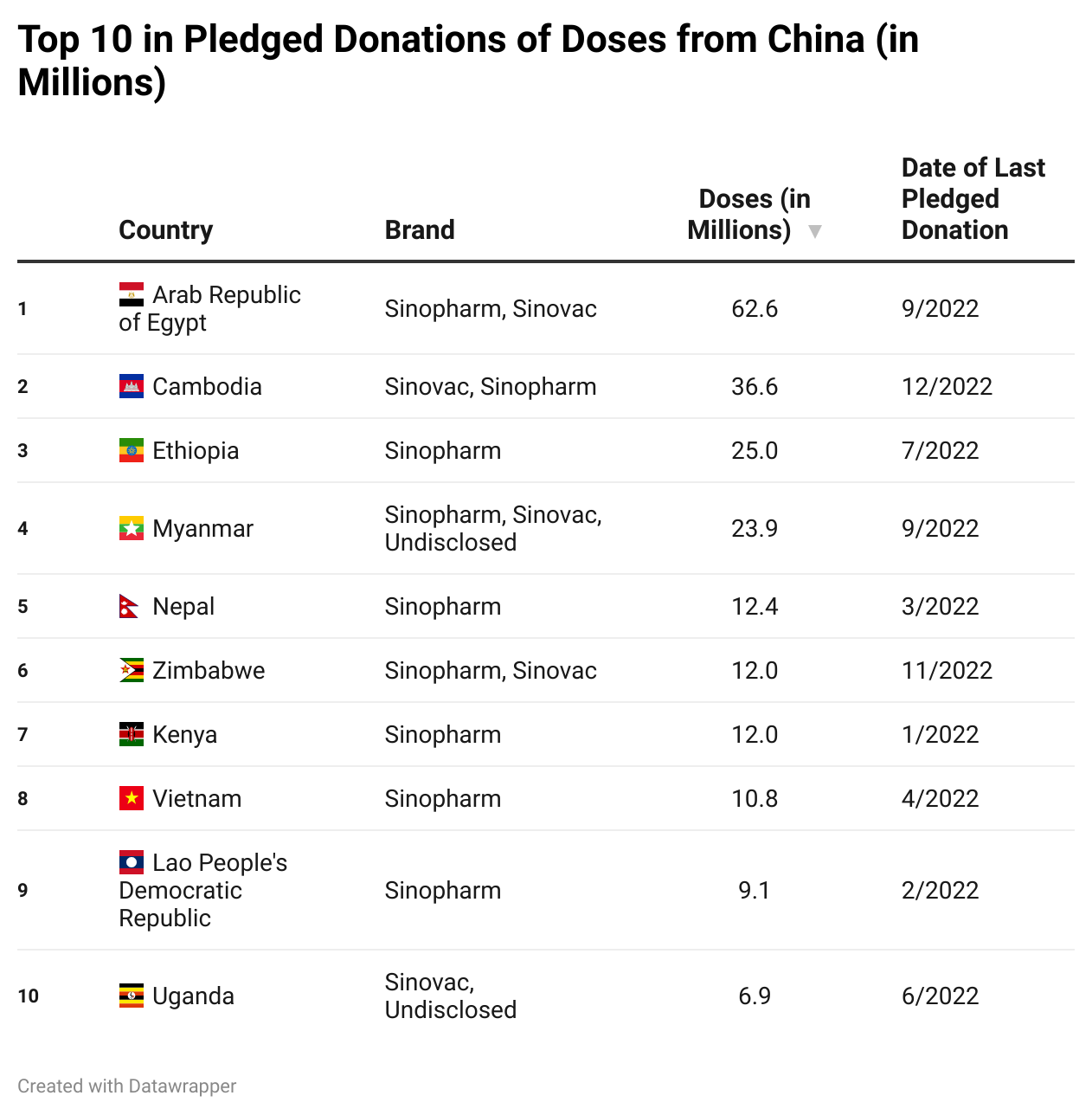
Top 10 Doses Delivered, Purchased, and Donated
Here is a slideshow that shows the countries that have received the most doses through deliveries, purchases, and donations.
Please press the arrows below to alternate between tables.
China’s Vaccines in Africa
As part of the South-South Cooperation, China pledged in late February 2021 to provide COVID-19 vaccines to 19 African countries. Following the 8th FOCAC Ministerial Meeting that took place on 30 November 2021, China made a new pledge to provide 1 billion doses of vaccines to Africa, including 600 million doses as donation and 400 million doses to be provided through such means as joint production by Chinese companies and relevant African countries. To date, 47 African countries have been receiving vaccines from China. While the pace of these deals has picked up on several occasions, China’s total number of vaccines delivered to Africa has constantly remained low.
Out of the 186 million doses sold and 80 million pledged donations to Africa, China has delivered 125 million, of which 31 million have been donations. However, issues of affordability and accessibility are particularly critical for African countries with limited financial resources at their disposal. Alongside bilateral agreements, Africa has also been receiving vaccines through the COVAX initiative.
China’s Vaccines in Latin America
Latin America has received the second-largest quantity of Chinese vaccines, despite only 22 countries having vaccine deals with China. Like Africa, Latin America and China are also working under the South-South Cooperation and the Belt and Road Initiative. While China has donated only 12 million doses to the region, it has sold 396 million doses, and to date, delivered 293 million doses. China also provides the region with active ingredients to make Chinese and other vaccines, such as the AstraZeneca vaccine.
Latin America plays an especially significant role to Chinese vaccine developer Sinovac, which has sold 230 million doses (out of 848 million doses sold globally) to 8 Latin American countries.
China’s Vaccines in Asia Pacific
Asia has received the most significant number of Chinese vaccines out of all regions in donations and sales. Thus far, the continent has received delivery of 890 million doses, out of the 938 million sold and 141 million donated. 97 million of the delivered doses have been donations.
In recent months, there has been a shift in the perception of Chinese vaccines in the region as local cases surge despite healthcare workers and citizens being inoculated with these vaccines. These surges have been attributed to the rise of the Delta and Omicron variants, which is more contagious, and the latter is able to evade immune protection from vaccines as well. In light of this, some countries are considering administering booster shots or mixing Chinese vaccines with other vaccine brands to enhance immunity, especially for vulnerable populations like the elderly and frontline workers.
- In November 2021, President Xi pledged an additional 150 million doses to be provided to the ASEAN bloc as well as $5 million to its COVID-19 response fund.
- In January 2022, at a virtual summit celebrating the 30th anniversary of diplomatic relations between China and five Central Asian countries (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan), President Xi pledged an additional 50 million vaccine doses to be donated to the region.
- In March 2022, at the 48th session of the Council of Foreign Ministers of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) in Pakistan, Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi pledged to provide an additional 300 million vaccine doses to Islamic countries and support the OIC’s member countries in Africa fighting the pandemic.
China’s Vaccines in Europe
As a region, Europe has received the fewest number of deliveries of Chinese vaccines. Thus far, only 59 million doses of Chinese vaccines have been delivered to 10 European countries, of which 5 million are donations. However, altogether China has sold 123 million doses to the region, most of which came from Turkey who penned a deal in November 2020 to buy 100 million doses of Sinovac. Turkey has redistributed doses via donations and sales to Bosnia and Herzegovina, Azerbaijan, Albania, and more.
One possible factor why Chinese vaccines are not widely used in European countries is because they have not yet received approval from the European Medicines Agency (EMA). The EMA is an agency of the European Union in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. However, national medical regulators may authorize the vaccines for emergency use which some Central and Eastern European countries have done.
China’s Multilateral Vaccine Contributions
In recent months, Chinese vaccines have been endorsed by an increasing list of international organizations, making these vaccines available through multilateral streams.
June 30, 2021. Gavi announced that it had signed an advance purchase agreement (APA) with Clover Biopharmaceuticals for its SCB-2019 protein-based adjuvanted vaccine, the R&D of which is funded by (CEPI), making up to 414 million doses available to participants of the COVAX Facility.
July 12, 2021. Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, announced that it had signed APAs with Sinopharm for its BBIBP-CorV inactivated virus vaccine and Sinovac for its CoronaVac inactivated virus vaccine. These agreements made 110 million doses immediately available to participants of the COVAX Facility, with options for additional doses, providing up to 550 million doses to the program.
February 8, 2022. CEPI, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, announced that it will expand its collaboration with Shanghai Zerun Bio and its parent company Walvax to advance the development of a COVID-19 variant vaccine. CEPI will invest up to an additional US$8.15 million to support a Phase I/II clinical trial in Mali which will evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of Zerun Bio’s prototype and multi-variant vaccine candidates.
March 22, 2022. The BRICS Vaccine R&D Center was launched as a joint effort between the five BRICS countries, and Sinovac took a leading role as the Chinese branch.
Chinese leaders have repeatedly emphasized that China wants to promote multilateral cooperation in the global response to COVID-19. China’s increasing participation in vital multilateral mechanisms is an encouraging step forward in fulfilling its promise of making Chinese COVID-19 vaccines a global public good and promoting multilateralism, on top of its many bilateral vaccine distribution deals.
COVAX Deliveries of Chinese Vaccines
COVAX is a partnership with CEPI, Gavi, the WHO, and UNICEF (a delivery partner). This initiatives has widened access to COVID-19 vaccines in an equitable manner, and also has improved the development and manufacturing of these vaccines. Read more about the initiative here.
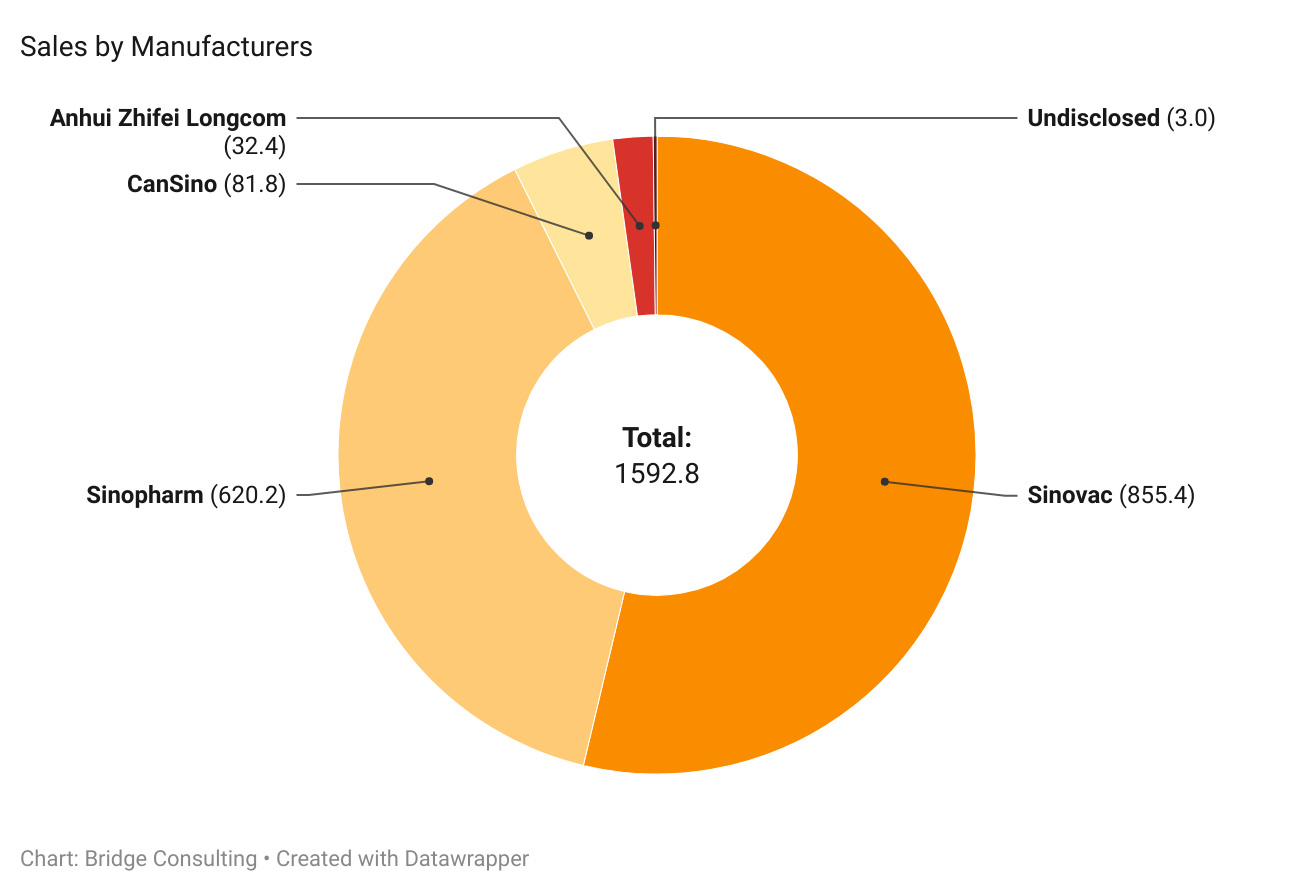
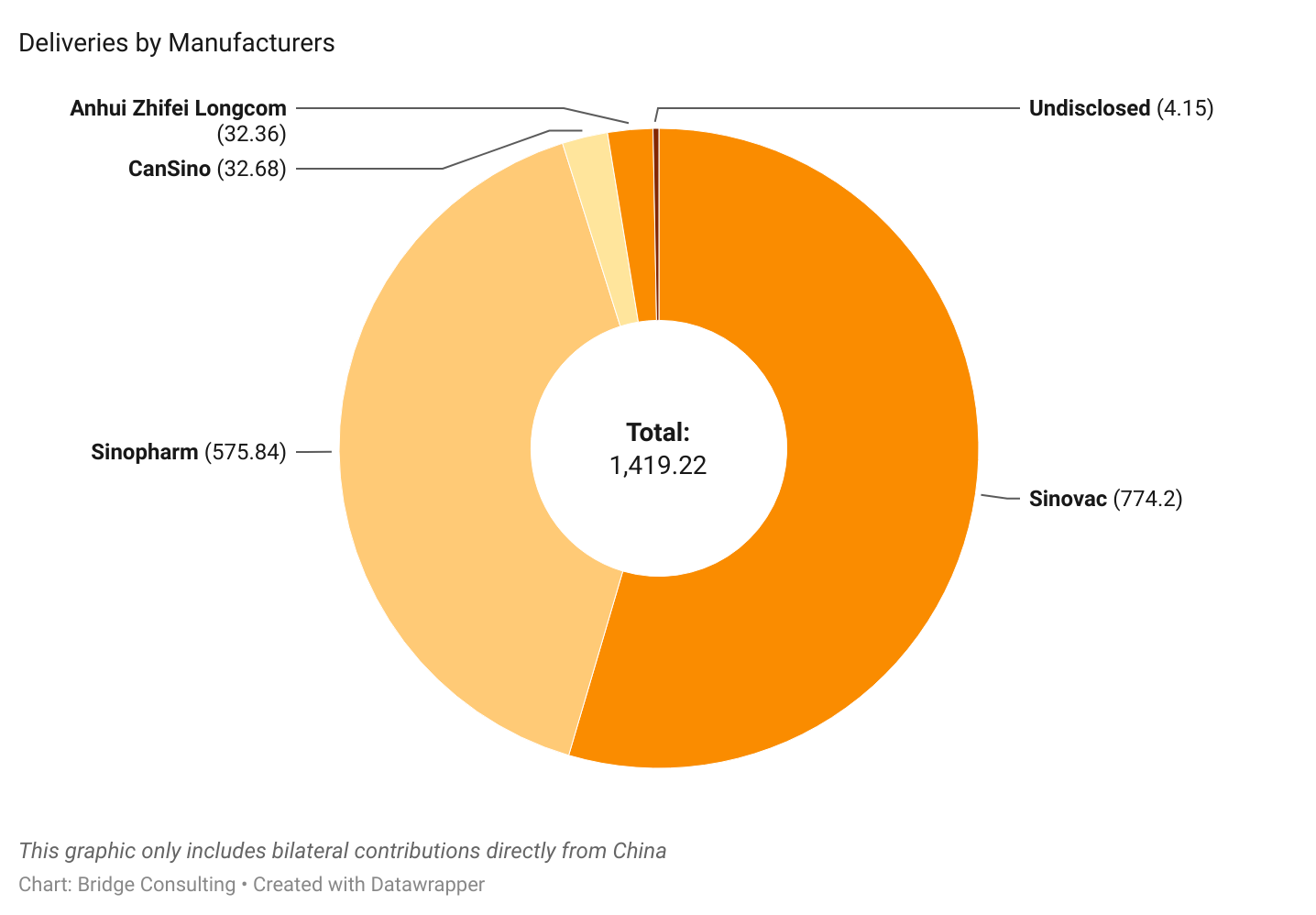
China’s Vaccines by Manufacturers
Sinopharm and Sinovac have been the most prominent manufacturers of Chinese COVID-19 vaccines sold and donated worldwide. Outside of these two, CanSino and Anhui Zhifei have also provided vaccines, though fewer.
Sinovac remains the leading supplier of vaccine sales by China, having sold 848 million doses and supplied vaccines to 48 countries in total. On the other hand, Sinopharm has been the leading supplier of vaccine donations from China, supplying 103 million doses of donated vaccines to 79 countries.
Take a look at our slideshow to see sales and deliveries of manufacturers. Please press the arrows below to alternate between graphs.
Sinovac – CoronaVac COVID-19 Vaccine
On June 1, 2021, the World Health Organization officially listed the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine developed by Chinese biopharmaceutical company Sinovac Biotech Ltd. for emergency use. This is the second Chinese COVID-19 vaccine to receive this approval after the inactivated Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine was approved for emergency use in May 2021.
Sinopharm – Beijing Bio-Institute of Biological Products Co-Ltd. (BBIBP) COVID-19 Vaccine
On May 7, the World Health Organization officially listed the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine developed by Beijing Bio-Institute of Biological Products Co-Ltd. (BBIBP) under the China National Pharmaceutical Group Corporation (Sinopharm) for emergency use, marking a significant milestone as the first Chinese COVID-19 vaccine to receive this approval.
CanSino – CONVIDECIA Ad5-nCoV-S recombinant vaccine
On May 19, 2022, the World Health Organization officially listed the CanSino (CONVIDECIA) vaccine developed by CanSino Biologics Inc., the Beijing Institute of Biotechnology, and the Academy of Military Medical Sciences for emergency use. This is the third vaccine developed by China to receive this approval. CanSino uses protein-coding technology delivered to the body by adenoviruses to create antibodies that fight COVID-19. This differs from the Sinovac and Sinopharm vaccines, which use the inactivated COVID-19 virus to generate an immune response against the disease.
Overseas Manufacturers of Chinese Vaccines
In addition to vaccine deliveries, Chinese COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers have been partnering with various developing countries to build up their local vaccine production capacities. At the Global Health Summit 2021, Chinese President Xi Jinping reiterated China’s support for its vaccine developers to transfer technologies to other developing countries and to carry out joint production. A total of 15 countries currently host vaccine joint production facilities: Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Pakistan, UAE, Uzbekistan, Serbia, Brazil, Chile, Columbia and Mexico.
Additional countries have only signed agreements but have not yet indicated production of vaccines or construction of vaccine facilities: Hungary, Russia, Bangladesh, Argentina, Turkey and Sri Lanka.
More Details on Overseas Manufacturers of Chinese Vaccines:
- Manufacturing of Chinese COVID-19 vaccines has started or is about to start for these countries.
-
- Algeria. Algerian pharmaceutical company Saidal received the green light to produce Sinovac vaccines domestically, with an aim to produce five million vaccine doses per month by January 2022 and to export vaccines to the rest of Africa. In late September 2021, Saidal started manufacturing the CoronaVac doses, with 20,000 produced in the first week, and by January 2022, was marketing the vaccine for sale. Currently, Saidal is producing vaccines at a rate of 60 million vaccines per year, however have stated that they can scale up production to 96 million vaccines per year depending on increased demand from other African countries.
- Brazil. The local Butantan Institute initially planned for 100% domestic production of COVID-19 vaccines in early 2022 . On March 25, 2022, Butantan finished construction and opened a new vaccine plant which was meant to create locally produced COVID-19 vaccines. Sinovac Coronavac vaccines were subsequently produced at this site. However, experts state that the plant may only produce other types of vaccines depending on the demands of Brazil’s government agencies. Production in the plant on a large scale is scheduled to start in early 2023. In late June, 2022, the Butantan Institute reported that they had officially ended production of the CoronaVac vaccine as of October 2021 due to a lack of demand. The last batch of 110 million doses was sent to Brazil’s Ministry of Health in February 2022.
- Cambodia. In May 2022, an MOU was signed between the Cambodian Pharmaceutical Enterprise and Sinovac for the construction of a vaccine packaging facility and license to fill and finish the Sinovac vaccines. The Cambodian government has already ordered over 104 million doses that the plant is projected to produce between 2024-2026.
- Chile. In August 2021, Sinovac formed a partnership with the Innovation Center of the Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, with the support of the government and the Millennium Institute for the planned construction of a fill-and-finish site near Santiago, a R&D research centre in the Antogafasta region and office spaces for scientists in the University. Construction for the vaccine plant started in May 2022 with an expected completion date in early 2023, considerably later than previous plans for the start of operations in the second quarter of 2022. It will have an estimated 50 million doses per year capacity while the R&D centre will benefit future development and production of other vaccines.
- Colombia. In August 2021, an MOE was signed between the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation and Sinovac for the packaging and filling of vaccines in the next 8 months following selection of a suitable plant, and a planned production of other vaccines over the next 2 years as part of a long-term plan to help Colombia rebuild its vaccine industry. In May 2022, Sinovac announced a USD $100 million investment for the project, including the construction of a vaccine plant in Bogotá with the capacity to package 50-60 million doses annually. Sinovac stated that the company is in the process of purchasing land in the country in order to create the vaccine plant.
- Egypt. Under an agreement with Sinovac, Egypt’s state-owned VACSERA company produced its first batch of 1 million doses of the VACSERA-Sinovac vaccine in July 2021 using raw materials from China. By February 2022, it has produced over 30 million doses of the vaccine. It plans to fill and finish 200 million doses a year for national needs, and build a second factory that can produce 3 million doses every day for regional export needs. This would make Egypt the largest vaccine producer in Africa and in the Middle East. In October 2021, they approved an increase of 250 million doses of raw materials to be sent for 2023. In January 2022, they also signed a new cooperation agreement for the construction of an automated vaccine cold storage facility at VACSERA that is projected to be able to hold 150 million vaccine doses. The construction of this facility started in April and was completed into operation on September 25, 2022. On the same day, 10 million doses of Sinovac vaccines donated by China became the first batch handled by the cold storage facility.
- Indonesia. On September 29, 2022, Indonesia’s National Agency of Drug and Food Control issued an Emergency Use Authorization for ‘AWcorna’ – an mRNA vaccine developed in China by Abogen-Yuxi Walvax. The AWcorna vaccine was registered by Jakarta-based bio-pharmaceuticals producer PT Etana Biotechnologies Indonesia (PT Etana). The vaccine will be locally produced by PT Etana through a vaccine-technology transfer with China. AWcorna received a halal fatwa (Islamic legal ruling on permits) from the Indonesian Ulema Council (MUI) and halal certification from the Halal Product Guarantee Agency (BPJPH). On October 7, Chinese Ambassador to Indonesia Lu Kang attended the opening ceremony of the vaccine manufacturing base which is the first mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine factory in Southeast Asia. The facility can achieve 100 million doses per year.
- Malaysia. On April 23, 2021, the filled-and-finished Sinovac vaccine by local company Pharmaniaga received conditional approval from Malaysia’s National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA), allowing its use in mass vaccinations. As of November, over 20 million doses have been supplied to the National Immunisation Programme in both manufactured and finished form, and the vaccine has been exported overseas to Myanmar. In a joint press conference with Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi, Malaysian Foreign Minister Saifuddin Abdullah emphasized that Malaysia and China would collaborate in vaccine research, development and production. The Malaysian government has discussed the possibility to setting up production plants in Malaysia with several Chinese vaccine manufactures.
- Mexico. Mexico partnered with Mexico to export active ingredients for its vaccines, which are then packaged in the country by Drugmex. CanSino stated that in 2021, it expected to make 1.2 million shots available per week to fulfil its agreement for 35 million doses. The deal was prematurely ended in May 2022 due to issues with meeting product delivery deadlines. Out of the 35 million doses in the deal, 14.1 million were completed.
- Morocco. On July 6, 2021, Morocco announced that their local pharmaceutical firm Sothema would soon be producing 5 million doses of Sinopharm per month under a fill-and-finish license. Morocco has started the production of more than three million doses of Sinopharm vaccine each month. The production capacity will reach five million doses starting from February 2022, and more than 20 million by the end of 2022.
- Myanmar. On December 13, 2021, Chairman of the State Administration Council and Prime Minister Senior General Min Aun Hlaing announced that Myanmar was currently looking to produce Chinese COVID-19 vaccines domestically. Joint production of Sinopharm vaccines, was planned to start from January with a target of producing five million units of vaccine per month. During April 29-30, 2022, Myanmar administered 1 million of the locally-produced ‘Myancopharm’ doses to individuals within the country.
- Pakistan. Pakistan’s National Institute of Health (NIH) partnered with CanSino to process its vaccines locally from bulk ingredients. Local media reported that locally filling vaccine vials will reduce the vaccine price by up to 30 percent. The locally finished ‘PakVac’ started national rollout in June 2021, and later in October, CanSino expressed their support for “enhancing the existing local filling and production capacity of the not only for Covid-19 vaccine but also for some other vaccines.”
- Serbia. On July 12, 2021, an official memorandum of understanding and cooperation was signed between Serbia, China, and the United Arab Emirates to co-finance and construct a vaccine-finishing factory in Serbia. The factory started construction in October 2021.
- United Arab Emirates. After hosting clinical trials of their vaccine, the UAE’s G42 launched a joint venture with Sinopharm to locally package the vaccine as ‘Hayat-Vax’ in March 2021. A new plant in the UAE, built in the Khalifa Industrial Zone of Abu Dhabi (KIZAD), will have a production capacity of 200 million doses a year with three filling lines and five automated packaging lines. Hayat-Vax has already been exported to countries including Kazakhstan and Vietnam. On June 30th, 2022, Ali Obaid Al Dhaheri (UAE Ambassador to China) met with Liu Jinchen (the President of Sinopharm) to discuss how to further collaborate regarding COVID-19 vaccines.
- Uzbekistan. In August 2021, Uzbek company Jurabek Laboratories JV LLC signed an agreement with China’s Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd to locally manufacture their vaccine, with an expected initial output of up to 10 million doses a month. It has rolled out the vaccines since October 2021.
- Several Chinese vaccine manufacturers have initial stage agreements (MOUs, license to produce vaccines, public statements of intent) with these countries, however have yet to deliver concrete results. We will continue to monitor the situation with these agreements.
-
- Argentina. In May 2021, Sinopharm and Argentinian pharmaceutical Sinergium Biotech agreed to produce vaccines in Argentina with discussions on technology transfer to follow. Political negotiations were initiated between the two countries regarding production, however no further updates have been announced.
- Bangladesh. Under a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between the government, China’s Sinopharm and Bangladesh’s Incepta pharmaceutical firm in August 2021, the local vaccine producer will supply five million doses of the vaccine a month from its plant in Savar. So far, production has yet to begin.
- Hungary. On September 10, 2021, Hungary’s government signed a letter of intent with Sinopharm executives to develop the required infrastructure within the next 10 months to produce the Chinese COVID-19 vaccine. No further updates regarding this have been announced.
- Nigeria. Cui Jianchun, Ambassador of the People’s Republic of China to Nigeria, announced on December 14, 2021, that China and Nigeria are currently undergoing talks regarding a potential collaboration to domestically produce Chinese COVID-19 vaccines.
- Russia. In 2020, CanSino carried out a phase 3 trial of its vaccine in partnership with Petrovax in Russia, and in August 2021, Petrovax agreed to partner with the developer to carry out local manufacturing. No further updates have been announced.
- Sri Lanka. In August 2021, Sinovac agreed to set up a manufacturing plant in Hambantota, Sri Lanka, with an initial plan to produce 13 million doses of the vaccine through Kelun Lifesciences. No further updates have been announced.
- Turkey. Turkey was one of the first five countries to receive a license to locally manufacture vaccines from Sinovac in May 2021. No further updates have been announced.
- Uganda. Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni met with Sinovac’s Ugandan representative and team in May 2022 to discuss plans for Sinovac to establish a vaccine and biotechnology centre in the country.
Notes
Additional information on procurements of Chinese vaccines:
MoreMethodology
This vaccine tracker is based entirely on data from reliable publicly accessible sources collected and compiled by Bridge Consulting with the help of Global Health Strategies (Brazil) and is updated every Monday by 7:00 PM (BJT GMT+8).
Where do we get our data?
Bridge collects and verifies data on Chinese vaccine sales, donations and deliveries every week. We source all our data from reliable, publicly accessible sources such as official government press releases, credible international and local news sources, and social media posts by government offices and verified officials.
How do you define ‘sales’, ‘donations’, ‘deliveries’?
Vaccine sales refers to the contractually committed vaccine doses that recipient countries have commercially purchased from Chinese vaccine developers.
Vaccine donations refers to the doses that a Chinese entity (government, vaccine developer, Red Cross etc.) has pledged to donate to a recipient country.
Vaccine deliveries refers to the doses that have physically been shipped from China to the recipient country.
How are countries and regions defined?
Our data is compiled and organized by country according to the United Nations’ M49 standard.
Why does our data change sometimes?
With the help of Global Health Strategies (Brazil), we constantly review our data for irregularities and correct them whenever new information becomes available.
Why does our data differ from other sources?
All our data is sourced manually by our team from publicly available sources. If you find that we have missed out on something, please let us know at vaccinetracker@bridgebeijing.com.